In an era where cyber threats are ever-evolving and traditional security perimeters no longer suffice, the Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments stands as a beacon of modern cybersecurity. This blog post delves into the transformative journey of zero-trust security, a model that challenges conventional wisdom and redefines how we protect our digital assets. Join us as we explore the principles, practices, and technologies that make zero-trust not just a strategy but a necessity for secure cloud computing.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Zero-Trust Architecture in cloud
In the realm of cybersecurity, Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a revolutionary concept that has gained significant traction. The term “Zero-Trust” reflects the principle that no entity, whether inside or outside the network’s perimeter, should be automatically trusted. Instead, every access request must be rigorously verified before granting entry.
The rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments is a response to the evolving threat landscape. As organizations migrate to the cloud, the traditional “castle-and-moat” security approach is becoming obsolete. Zero-trust is not merely a technology but a holistic approach to network security that encompasses identity verification, endpoint security, and least privilege access control.
The core idea behind zero-trust is simple: trust no one, verify everyone. This means continuous monitoring and validation of every request to access any resource. It’s a shift from the outdated notion that everything behind the corporate firewall is safe. The focus keyword, “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments,” encapsulates this shift towards a more dynamic and adaptive security posture.
Understanding zero-trust architecture is essential for anyone involved in cloud security. It’s not just about adopting new technologies but also about changing the mindset and culture within an organization. As we delve deeper into the topic, we’ll explore the components, benefits, and implementation strategies of zero-trust architecture, providing readers with a comprehensive overview of this transformative security model.
Historical Context: The Evolution of Network Security
Defining Zero-Trust: Principles and Components
The evolution of network security is a tale of adapting to ever-changing threats. In the early days of computing, security was a minimal concern, with systems operating in isolated environments. However, as the internet burgeoned, so did the need for robust security measures.
Initially, network security focused on creating strong perimeters around networks—firewalls and antivirus software were the main lines of defense. This “castle-and-moat” approach was predicated on the idea that threats came from outside the network, and once inside, users were generally trusted.
But as technology advanced, so did the sophistication of cyber threats. Hackers began exploiting vulnerabilities within the network, and the rise of mobile devices, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) further blurred the boundaries of the traditional network perimeter. The perimeter-based model proved inadequate in protecting against insider threats and sophisticated cyber attacks.
Enter Zero-Trust Architecture—a paradigm shift in network security. This approach assumes that threats exist both outside and inside the network. The focus keyword, “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments,” signifies a move away from the outdated trust model to one that requires continuous verification of all users and devices, regardless of their location.
The historical context of network security underscores the necessity of zero-trust principles in today’s cloud-centric world. It’s a response to a landscape where the only constant is change, and trust can no longer be a given. As we continue to explore zero-trust architecture, we’ll see how it’s not just a trend but a fundamental rethinking of network security to meet the demands of modern computing.
Why Zero-Trust Matters in Cloud Environments
In the digital age, where data breaches are commonplace and cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, the importance of Zero-Trust Architecture in cloud environments cannot be overstated. The focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” highlights a critical shift in cybersecurity mindset.
Cloud environments are inherently different from traditional on-premises networks. They are dynamic, scalable, and often span multiple service providers. This complexity introduces unique security challenges, as the traditional network perimeter dissolves, making it harder to monitor and control access.
Zero-trust matters in cloud environments because it addresses these challenges head-on. It operates on the principle that trust is a vulnerability. In a zero-trust model, every access request is treated as if it originates from an untrusted network. This means:
- Continuous Verification: Every user and device is authenticated and authorized before accessing cloud resources.
- Least Privilege Access: Users are granted the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks, reducing the risk of insider threats and lateral movement by attackers.
- Microsegmentation: The network is divided into small, secure zones to contain breaches and limit the attacker’s movement.
By implementing zero-trust principles, organizations can create a more secure cloud environment that adapts to the fluid nature of cloud resources and user access. It’s not just about deploying new technologies; it’s about adopting a new security framework that is robust, flexible, and capable of defending against modern cyber threats.
The rise of zero-trust architecture is a testament to its effectiveness in protecting cloud environments. As organizations continue to embrace cloud computing, zero-trust becomes not just an option but a necessity for ensuring the security and integrity of their data and systems. It’s a proactive approach to security that aligns with the evolving landscape of cloud computing.
The Shift from Perimeter-Based to Zero-Trust Security
The cybersecurity landscape has undergone a significant transformation with the shift from perimeter-based security to Zero-Trust Security. This change is encapsulated in the focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments,” highlighting a strategic move to a more resilient security framework.
Perimeter-based security, often likened to a fortress with high walls, was predicated on the assumption that threats were predominantly external. The defenses were focused on keeping malicious actors out, but once inside, users generally had broad access, which posed a significant risk.
Zero-Trust Security dismantles this notion by operating on a ‘never trust, always verify’ principle. It recognizes that threats can originate from anywhere and that the traditional network boundary is no longer sufficient in the era of cloud computing, remote work, and mobile access.
The transition to zero-trust involves:
- Identity Verification: Robust authentication mechanisms ensure that only verified users and devices can access network resources.
- Microsegmentation: Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network.
- Least Privilege Access: Granting users the minimum level of access required to perform their duties, thereby reducing the attack surface.
This shift is crucial in cloud environments where resources are accessed over the internet, and traditional security perimeters are ineffective. Zero-trust security provides a framework that adapts to the complexity and fluidity of cloud architectures, offering a more granular and dynamic approach to securing assets.
Embracing zero-trust is not just about deploying new technologies; it’s about a fundamental change in how organizations approach security. It requires a cultural shift towards continuous monitoring, assessment, and adjustment of security controls.
The rise of zero-trust security represents a proactive and pragmatic response to modern cybersecurity challenges. It’s an approach that aligns with the realities of today’s interconnected world, where the only constant is change, and trust is a vulnerability that can be exploited. By adopting zero-trust principles, organizations can enhance their security posture and better protect their cloud environments against a wide array of cyber threats.
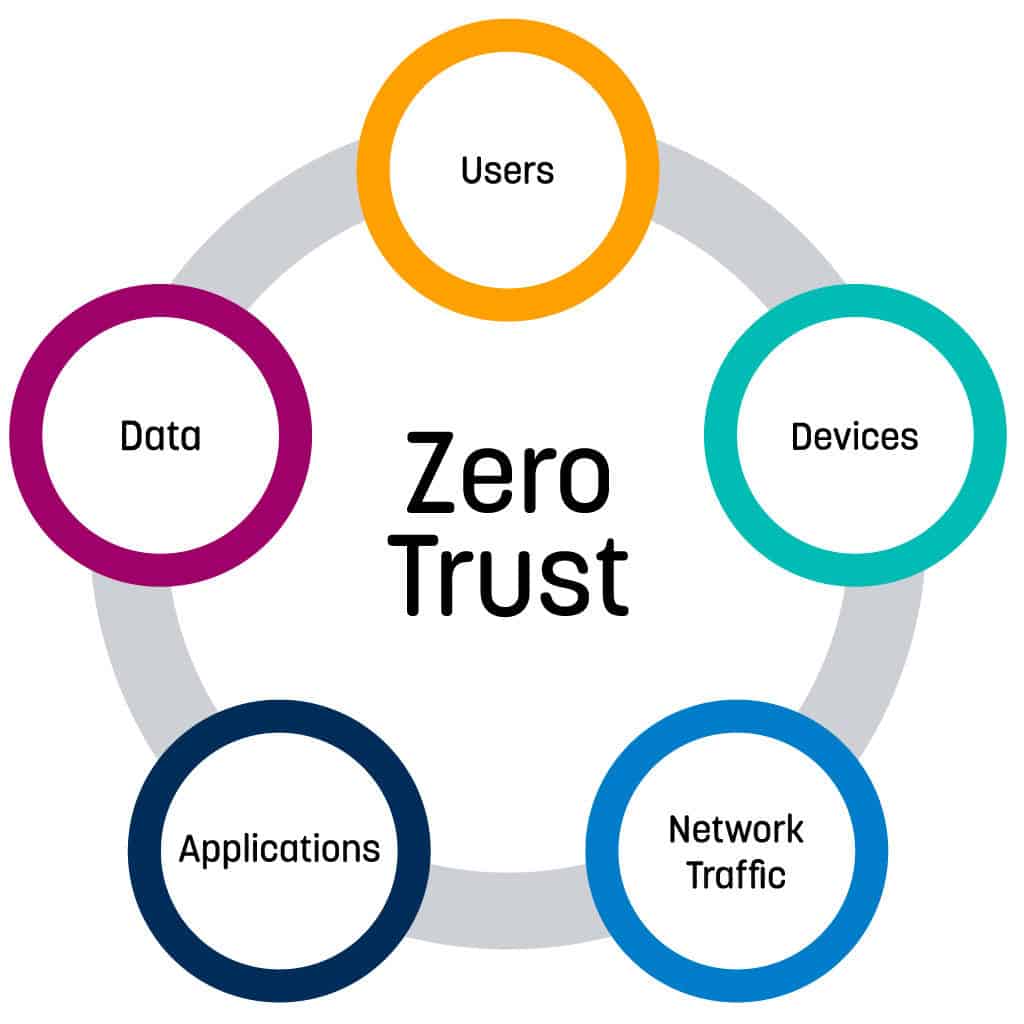
Key Drivers for Adopting Zero-Trust in the Cloud
The adoption of Zero-Trust Architecture in cloud environments is driven by several key factors that reflect the changing landscape of cybersecurity. The focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” underscores the urgency and importance of these drivers:
- Increased Cyber Threats: As cyber threats grow in number and sophistication, traditional security measures are no longer sufficient. Zero-trust offers a more robust defense by verifying every access request, regardless of its origin.
- Cloud Migration: The shift to cloud-based services has dissolved the traditional network perimeter. Zero-trust is essential in such environments where resources are accessed remotely and the distinction between internal and external is blurred.
- Remote Workforce: The rise of remote work has introduced new security challenges. Zero-trust secures remote access by ensuring that all users, whether in-office or remote, are consistently verified and granted the least privilege necessary.
- Regulatory Compliance: With regulations like GDPR and HIPAA imposing strict data protection requirements, zero-trust helps organizations meet compliance demands by providing a framework for securing sensitive data.
- Digital Transformation: As organizations undergo digital transformation, they require a security model that can accommodate rapid change and innovation. Zero-trust architecture is flexible and scalable, making it ideal for dynamic cloud environments.
- Insider Threats: Zero-trust mitigates the risk of insider threats by enforcing strict access controls and monitoring internal activities, ensuring that users can only access the resources they are authorized for.
These drivers highlight why “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” is not just a trend but a strategic imperative for organizations looking to secure their cloud infrastructure and protect against the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Zero-Trust and Regulatory Compliance
In the context of regulatory compliance, Zero-Trust Architecture plays a pivotal role. The focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” is particularly relevant as organizations worldwide are required to adhere to stringent data protection laws.
Regulatory frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, and many others, mandate that organizations implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data. Zero-trust aligns with these requirements by enforcing strict access controls and ensuring that data is accessed securely and appropriately.
Here’s why zero-trust and regulatory compliance go hand-in-hand:
- Data Protection: Zero-trust minimizes the risk of data breaches by verifying every access request and ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information.
- Access Control: It enforces the principle of least privilege, which is often a requirement in regulatory standards, ensuring users have access only to the data necessary for their role.
- Audit Trails: Zero-trust architectures facilitate detailed logging and monitoring, which are crucial for compliance reporting and audits.
- Risk Management: By segmenting the network and applying consistent security policies, zero-trust helps in identifying and managing risks more effectively.
Adopting a zero-trust model demonstrates an organization’s commitment to security and compliance, showing that they are taking proactive steps to protect customer and patient data. As regulations continue to evolve, “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” will likely become even more integral to meeting these legal obligations. It’s a forward-thinking approach that not only secures data but also aligns with global compliance standards, making it an essential strategy for any organization operating in the cloud.
Implementing Zero-Trust: A Step-by-Step Approach
Implementing Zero-Trust Architecture in cloud environments is a strategic process that involves several key steps. The focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” emphasizes the growing importance of this security model. Here’s a step-by-step approach to guide you through the implementation:
- Identify Sensitive Data: Begin by locating where your sensitive data resides. This could be in cloud storage, databases, or applications.
- Map the Transaction Flows: Understand how data moves within your organization. This includes user access patterns and data workflows.
- Architect a Zero-Trust Network: Design your network with microsegmentation in mind, creating zones that segregate different types of data and services.
- Establish Trust Zones: Define trust zones based on the sensitivity of the data and the level of access required by different user groups.
- Enforce Access Control Policies: Implement strict access control policies that adhere to the principle of least privilege.
- Authenticate and Authorize: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and identity and access management (IAM) solutions to verify every user and device.
- Monitor and Maintain: Continuously monitor network activity and maintain the zero-trust policies, adjusting as necessary to respond to new threats.
- Educate and Train: Ensure that all stakeholders understand the principles of zero-trust and are trained on the new security protocols.
- Evaluate and Adapt: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your zero-trust architecture and adapt to technological advancements and evolving threats.
By following these steps, you can effectively implement a zero-trust model in your cloud environment, enhancing your organization’s security posture and resilience against cyber threats. Remember, zero-trust is not a one-time project but an ongoing journey that requires continuous evaluation and adaptation.
Technologies Enabling Zero-Trust Architecture
The successful implementation of Zero-Trust Architecture in cloud environments is heavily reliant on a suite of technologies designed to enforce its core principles. The focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” underscores the critical role these technologies play.
Here are some of the key technologies enabling zero-trust:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM solutions are fundamental to zero-trust, providing robust user authentication and ensuring that only authorized individuals can access certain resources.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to resources, thus reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access.
- Microsegmentation: This technology divides the network into secure and manageable segments, allowing organizations to control access to specific areas and reduce the attack surface.
- Least Privilege Access Control: Systems that enforce least privilege ensure users have access only to the resources they need for their specific roles, minimizing the potential impact of a breach.
- Endpoint Security: With the proliferation of devices accessing the network, endpoint security solutions are crucial for ensuring that all devices are secure and compliant with security policies.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware, helping to detect and respond to threats quickly.
- Encryption: Protecting data both at rest and in transit, encryption is a critical component of zero-trust, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure.
- Network Access Control (NAC): NAC solutions help to enforce zero-trust policies by controlling the access of devices to the network based on compliance with security policies.
These technologies form the backbone of Zero-Trust Architecture, creating a secure environment where trust is earned, not given. As the focus keyword suggests, the rise of zero-trust in cloud environments is supported by these advanced technologies, which together provide a robust framework for protecting against modern cyber threats.
Challenges and Considerations in Zero-Trust Adoption
Adopting Zero-Trust Architecture in cloud environments comes with its set of challenges and considerations. The focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” not only highlights the increasing adoption of this security model but also brings attention to the hurdles organizations may face during its implementation.
Here are some key challenges and considerations:
- Cultural Shift: Zero-trust requires a fundamental change in organizational mindset. Moving from a trust-based to a verify-based culture can be difficult, as it demands a new approach to security practices and policies.
- Complexity: Implementing zero-trust can be complex, particularly in diverse and hybrid cloud environments. It requires careful planning and a deep understanding of the network architecture and data flows.
- Legacy Systems: Older systems may not be compatible with zero-trust principles, and upgrading or replacing them can be costly and time-consuming.
- User Experience: Balancing security with user convenience is crucial. Overly stringent controls can hinder productivity and frustrate users, leading to resistance against the new security measures.
- Continuous Monitoring: Zero-trust necessitates continuous monitoring and validation of users and devices, which can be resource-intensive.
- Integration: Integrating various security technologies to work cohesively under a zero-trust framework can be challenging.
- Skills Gap: There may be a skills gap in the workforce, as zero-trust architecture requires knowledge of the latest security technologies and practices.
Despite these challenges, the adoption of zero-trust is essential for securing cloud environments. Organizations must weigh these considerations carefully and develop a strategic plan to overcome them. With the right approach, the transition to zero-trust can lead to a significantly more secure and resilient infrastructure.
Case Studies: Zero-Trust in Action
Exploring case studies is an effective way to understand the practical application and benefits of Zero-Trust Architecture in cloud environments. The focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” emphasizes the real-world impact of this security model. Here, we’ll look at how organizations have successfully implemented zero-trust principles.
Financial Services Firm Embraces Zero-Trust
A leading financial services firm faced challenges with securing client data and meeting compliance standards. By adopting a zero-trust model, they were able to:
- Implement strong identity verification processes.
- Apply microsegmentation to protect critical assets.
- Achieve a significant reduction in the risk of data breaches.
Healthcare Provider Secures Patient Data
A healthcare provider needed to ensure the security of sensitive patient records while allowing access to authorized personnel. Zero-trust enabled them to:
- Enforce strict access controls based on user roles.
- Utilize encryption for data at rest and in transit.
- Monitor access patterns and quickly respond to anomalies.
Retail Giant Prevents Data Leaks
A global retail company implemented zero-trust to protect against insider threats and secure customer information. Their zero-trust strategy included:
- Continuous monitoring of all network activity.
- Least privilege access controls for all staff.
- Real-time threat detection and response mechanisms.
These case studies demonstrate “Zero-Trust in Action” and highlight the effectiveness of zero-trust architecture in enhancing security across various industries. By learning from these examples, organizations can better understand how to apply zero-trust principles to their own cloud environments. The rise of zero-trust is not just a theoretical concept but a practical solution that organizations are actively implementing to safeguard their digital asset
Future Trends: Zero-Trust and Emerging Technologies
Here are some emerging trends at the intersection of zero-trust and new technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML are becoming integral to zero-trust, offering advanced analytics to detect anomalies and automate real-time security decisions.
- Blockchain for Identity Verification: Blockchain technology has the potential to provide a decentralized and tamper-proof method for identity verification, enhancing the trustworthiness of zero-trust systems.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Security: As IoT devices proliferate, zero-trust principles are crucial for ensuring that each device is authenticated and its communications are secure.
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE): SASE combines network security functions with WAN capabilities to support the dynamic, secure access needs of organizations, aligning with zero-trust principles.
- 5G Networks: The rollout of 5G will increase the speed and volume of data transfer, and zero-trust architectures will be essential to secure these high-speed networks.
- Quantum Computing: Although still in its infancy, quantum computing could revolutionize encryption and security. Zero-trust models will need to evolve to harness and secure quantum technologies.
The future of zero-trust is one of continuous evolution, driven by technological advancements and the ever-changing threat landscape. Organizations that stay abreast of these trends and incorporate them into their zero-trust strategies will be well-positioned to protect their assets in the cloud and beyond. The rise of zero-trust architecture is not just a current phenomenon but a long-term shift towards a more secure digital world.
Best Practices for Zero-Trust Security
Adopting Zero-Trust Security is a strategic move for organizations aiming to fortify their cloud environments. The focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” highlights the importance of implementing this model effectively. Here are some best practices to ensure a successful zero-trust security posture:
- Start with a Clear Strategy: Define what zero-trust means for your organization. Understand your assets, workflows, and security requirements to create a tailored zero-trust strategy.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users and devices the minimum access necessary to perform their functions. Regularly review permissions and adjust them as needed.
- Verify Explicitly: Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points, such as user identity, location, device health, service or workload, data classification, and anomalies.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Strengthen your security with MFA. It’s one of the simplest and most effective ways to increase security against credential theft.
- Microsegmentation: Segment your network to contain breaches and limit lateral movement. Define security controls at the micro-level to protect individual assets.
- Monitor and Log Activity: Implement comprehensive monitoring and logging to detect suspicious activities and respond to them promptly.
- Automate Security Policies: Use automation to enforce security policies consistently. Automation helps in reducing human error and response times to threats.
- Educate Your Workforce: Train employees on the principles of zero-trust security. Awareness is key to preventing accidental breaches.
- Regularly Update and Patch: Keep all systems up to date with the latest security patches to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Continuous Compliance: Ensure that your zero-trust practices align with industry regulations and standards for data protection and privacy.
- Embrace a Holistic Approach: Zero-trust is not just a set of tools; it’s a comprehensive approach that includes policies, processes, and technologies working together.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively implement Zero-Trust Security and enhance their defenses against the sophisticated threats present in today’s cloud environments. The rise of zero-trust architecture is a testament to its necessity and effectiveness in the modern cybersecurity landscape.
Zero-Trust Architecture: Myths vs. Reality
As Zero-Trust Architecture gains prominence in cloud environments, it’s important to distinguish between myths and reality. The focus keyword “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments” invites us to dispel misconceptions and understand the true essence of zero-trust.
Myth: Zero-Trust Is Only for Large Enterprises
Reality: Zero-trust is scalable and can be implemented by organizations of all sizes. It’s about principles and practices that apply whether you’re a small business or a multinational corporation.
Myth: Zero-Trust Complicates User Experience
Reality: While zero-trust does require robust authentication, it can be user-friendly. Single Sign-On (SSO) and adaptive authentication can streamline the process without compromising security.
Myth: Zero-Trust Is Just About Technology
Reality: Zero-trust is as much about policies and culture as it is about technology. It requires a holistic approach that includes educating employees and establishing clear security protocols.
Myth: Zero-Trust Is a Single Solution
Reality: Zero-trust is not a product you can purchase; it’s a security framework that involves integrating various technologies and strategies to create a comprehensive defense system.
Myth: Once Implemented, Zero-Trust Is Set and Forget
Reality: Zero-trust requires ongoing management and adaptation. As threats evolve and new technologies emerge, zero-trust architectures must be continuously reviewed and updated.
Understanding these myths and realities is crucial for anyone considering “The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments.” It’s a strategy that demands commitment and a clear understanding of its principles to be effectively implemented and maintained.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Journey of Zero-Trust Security
Zero-trust is not a destination but a continuous path of adaptation and improvement. It requires diligence, foresight, and a willingness to evolve. Here are some key takeaways for the road ahead:
- Stay Informed: The cybersecurity landscape is ever-changing. Staying informed about the latest threats and trends is crucial for maintaining an effective zero-trust posture.
- Be Proactive: Don’t wait for a breach to occur. Proactively assess and improve your security measures, anticipating potential vulnerabilities and addressing them before they are exploited.
- Foster Collaboration: Zero-trust security is a collaborative effort. Encourage open communication and cooperation between IT, security teams, and other departments.
- Embrace Innovation: Leverage emerging technologies and innovative practices to enhance your zero-trust architecture. Be open to new ideas that can strengthen your security.
- Prioritize Education: Continuous education and training for all stakeholders are vital. A well-informed team is your best defense against security breaches.
- Review and Revise: Regularly review your security policies and practices. Be prepared to revise them in response to new information or changes in the environment.
The rise of zero-trust security is a testament to its necessity in the face of modern challenges. As organizations continue to migrate to the cloud and embrace digital transformation, zero-trust provides a framework that not only addresses current security needs but also lays the foundation for future advancements.
In essence, zero-trust is about never resting on your laurels. It’s about constant vigilance and a commitment to security that matches the pace of technological change. The journey of zero-trust security is one that evolves with the times, ensuring that organizations can confidently face the threats of today and tomorrow.
Embracing the Future with Zero-Trust Security
As we reach the end of our journey through the intricacies of Zero-Trust Architecture, it’s evident that this is not just a fleeting trend but a fundamental shift in how we approach security in cloud environments. The rise of zero-trust is a clear response to the complex challenges and threats that modern organizations face in an increasingly cloud-centric world.
The adoption of zero-trust is an ongoing process, one that requires commitment, foresight, and a willingness to continuously adapt. It’s about building a security culture that is proactive, informed, and collaborative. As we’ve seen, zero-trust is not a one-size-fits-all solution but a strategic framework that must be tailored to the unique needs and contexts of each organization.
In conclusion, the future of cybersecurity is dynamic and uncertain, but one thing remains clear: the principles of zero-trust offer a path forward that can help organizations navigate this uncertainty with confidence. By embracing zero-trust, we can create more resilient, agile, and secure cloud environments that are prepared to meet the challenges of today and tomorrow.
The journey of zero-trust security is one of continuous evolution, and as we look ahead, it’s an exciting time to be part of this transformative movement. Let’s continue to learn, innovate, and secure our digital world, together.
Thank you for following along with this comprehensive guide on Zero-Trust Architecture. May your path to a more secure cloud environment be successful and enlightening. Remember, in the world of cybersecurity, trust is not given; it is earned and verified, every step of the way.




Pingback: Understanding the Impact of 5G on Network Security - EstoreAB
Pingback: Chronicles of the Cloud: Exploring IT Innovations - EstoreAB