Palo Alto Firewalls: Safeguarding Networks Against Vulnerabilities
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, organizations rely on robust defenses to protect their digital assets. Enter Palo Alto Firewalls—powerful sentinels that stand guard against threats, vulnerabilities, and malicious actors. In this comprehensive blog post, we explore the intricacies of Palo Alto Firewalls, dissect real-world vulnerability examples, and provide actionable insights for securing your network. Whether you’re a seasoned security professional or a curious learner, join us on this journey through firewalls, vulnerabilities, and resilience.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Palo Alto Firewalls
Palo Alto Firewalls are renowned for their robust security features and advanced threat prevention capabilities. As organizations increasingly rely on digital infrastructure, the need for effective network security solutions has never been greater. Palo Alto Networks, a leader in the cybersecurity industry, offers a range of next-generation firewalls designed to protect networks from cyber threats, including vulnerabilities.
Why Palo Alto Firewalls Matter
Palo Alto Firewalls go beyond traditional firewall functionalities. They combine stateful inspection, intrusion prevention, application awareness, and user-based policies to create a comprehensive security ecosystem. Here’s why they matter:
- Advanced Threat Prevention: Palo Alto Firewalls use a combination of signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, and machine learning to identify and block known and unknown threats. Their threat prevention capabilities extend to malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and more.
- Application Visibility and Control: Palo Alto Firewalls provide granular visibility into network traffic, allowing administrators to identify applications, users, and content. This visibility enables precise policy enforcement and helps prevent unauthorized application usage.
- User-Based Policies: Palo Alto Firewalls allow policies based on user identities, not just IP addresses. This user-centric approach ensures that security rules adapt to individual user behavior, enhancing overall protection.
- Integration with Threat Intelligence: Palo Alto Firewalls can integrate with threat intelligence feeds, providing real-time updates on emerging threats. This proactive approach helps organizations stay ahead of vulnerabilities.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Palo Alto Firewalls include WAF features that protect web applications from common vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and remote file inclusion.
Vulnerabilities and Palo Alto Firewalls
While Palo Alto Firewalls are robust, no system is entirely immune to vulnerabilities. Regular security assessments, patch management, and adherence to best practices are essential to minimize risks. In our subsequent sections, we’ll delve deeper into common vulnerabilities, security patch management, and configuration best practices for Palo Alto Firewalls.
In summary, Palo Alto Firewalls play a critical role in safeguarding networks against cyber threats. Their focus on threat prevention, user-centric policies, and integration with threat intelligence makes them a valuable asset for organizations seeking robust security solutions. Let’s explore these features further in the upcoming sections of this blog post
Understanding Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses or flaws in software, hardware, or network systems that can be exploited by malicious actors. In the context of Palo Alto Firewalls, understanding vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining a secure network infrastructure.
Types of Vulnerabilities
- Software Vulnerabilities: These are coding errors, design flaws, or configuration mistakes within the firewall’s operating system or applications. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access, execute arbitrary code, or disrupt services.
- Configuration Vulnerabilities: Misconfigured firewall rules, open ports, or weak authentication settings can create vulnerabilities. For example, leaving default credentials unchanged or allowing unnecessary services can expose Palo Alto Firewalls to risks.
- Firmware Vulnerabilities: Firewalls rely on firmware (embedded software) for functionality. Outdated or unpatched firmware may contain vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Regular firmware updates are essential.
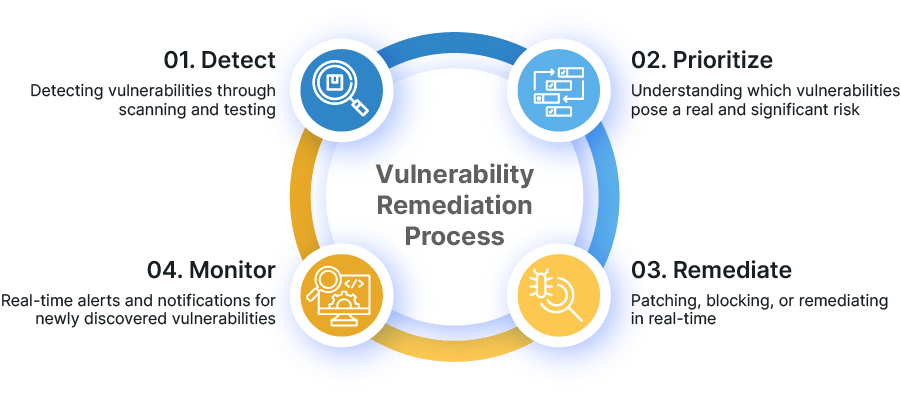
Impact of Vulnerabilities
- Security Breaches: Exploited vulnerabilities can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, or network compromise. For Palo Alto Firewalls, this could mean unauthorized traffic passing through or compromised user credentials.
- Service Disruption: Vulnerabilities may allow attackers to disrupt firewall services, affecting network availability. Downtime can impact business operations and productivity.
- Malware Propagation: If a vulnerability allows malware to bypass the firewall, it can spread within the network, affecting other devices.
Mitigating Vulnerabilities
- Patch Management: Regularly update Palo Alto Firewalls with security patches. Palo Alto Networks releases patches to address known vulnerabilities. Apply these promptly.
- Configuration Audits: Regularly review firewall configurations to identify and rectify misconfigurations. Follow best practices for rule management.
- Threat Intelligence: Leverage threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about emerging vulnerabilities. Palo Alto Firewalls can integrate with threat feeds for real-time updates.
- User Training: Educate users about security best practices. Avoid risky behavior, such as clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files.
Common Vulnerabilities in Palo Alto Firewalls
Palo Alto Firewalls are powerful security solutions, but like any technology, they are not immune to vulnerabilities. In this section, we’ll explore common weaknesses that organizations should be aware of when deploying Palo Alto Firewalls.
1. Software Vulnerabilities
Software vulnerabilities are coding errors or design flaws within the firewall’s operating system or applications. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access or compromise the firewall’s functionality. Palo Alto regularly releases security patches to address known software vulnerabilities. Organizations must promptly apply these updates to minimize risks.
2. Configuration Vulnerabilities
Misconfigured firewall rules, open ports, or weak authentication settings can create vulnerabilities. Leaving default credentials unchanged or allowing unnecessary services can expose Palo Alto Firewalls to risks. Regular configuration audits are essential to identify and rectify misconfigurations. Following best practices for rule management ensures a more secure setup.
3. Firmware Vulnerabilities
Firewalls rely on firmware (embedded software) for functionality. Outdated or unpatched firmware may contain vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Regularly updating firmware is crucial. Palo Alto Networks provides firmware updates to address security issues and enhance overall resilience.
4. Impact of Vulnerabilities
- Security Breaches: Exploited vulnerabilities can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, or network compromise. For Palo Alto Firewalls, this could mean unauthorized traffic passing through or compromised user credentials.
- Service Disruption: Vulnerabilities may allow attackers to disrupt firewall services, affecting network availability. Downtime can impact business operations and productivity.
- Malware Propagation: If a vulnerability allows malware to bypass the firewall, it can spread within the network, affecting other devices.
5. Mitigating Vulnerabilities
- Patch Management: Regularly update Palo Alto Firewalls with security patches. Timely patching reduces the window of vulnerability.
- Configuration Audits: Review firewall configurations to identify and rectify misconfigurations. Follow best practices for rule management.
- Threat Intelligence: Leverage threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about emerging vulnerabilities. Palo Alto Firewalls can integrate with threat feeds for real-time updates.
- User Training: Educate users about security best practices. Avoid risky behavior, such as clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files.
In summary, understanding vulnerabilities and implementing proactive measures are essential for maintaining a secure Palo Alto Firewall deployment. By addressing vulnerabilities promptly and following security best practices, organizations can enhance their network defenses and protect critical assets. Stay vigilant and prioritize security
Security Patch Management
Palo Alto Firewalls are powerful guardians of network security, but even the mightiest walls can develop cracks. In this section, we’ll explore the critical aspect of security patch management for Palo Alto Firewalls.
The Importance of Patching
- Vulnerability Mitigation: Security patches address known vulnerabilities. By applying them promptly, you reduce the attack surface and protect your network.
- Stay Ahead of Threats: Cyber threats evolve constantly. Regular patching ensures that your Palo Alto Firewall is equipped to fend off the latest attacks.
- Performance Optimization: Patches often include performance enhancements and bug fixes. Keeping your firewall up-to-date ensures optimal functionality.
Best Practices for Patch Management
- Scheduled Updates: Set up a regular patching schedule. Palo Alto Networks releases patches periodically—stay informed and plan accordingly.
- Test Before Deployment: Test patches in a controlled environment before rolling them out to production firewalls. Ensure compatibility with your existing configurations.
- Backup Configurations: Always back up your firewall configurations before applying patches. In case of issues, you can revert to a known working state.
- Automate When Possible: Use automation tools to streamline patch deployment. This reduces manual effort and minimizes the window of vulnerability.
Handling Emergency Patches
- Critical Vulnerabilities: If Palo Alto Networks releases an emergency patch for a critical vulnerability, prioritize it. Immediate action is crucial.
- Communication: Inform relevant stakeholders about emergency patches. Coordinate with your team to apply them swiftly.
Configuration Best Practices
Configuring Palo Alto Firewalls correctly is essential for maintaining a secure network environment. Let’s explore some best practices to enhance the effectiveness of your Palo Alto Firewall deployment.
1. Segmentation and Zones
- Create Security Zones: Divide your network into logical security zones (e.g., DMZ, internal, external). Assign interfaces to these zones based on their purpose (e.g., servers, users, IoT devices).
- Implement Inter-Zone Policies: Define policies that control traffic between zones. Limit unnecessary communication and enforce strict access controls.
2. Rule Management
- Rule Order Matters: Arrange security rules in order of evaluation. Place more specific rules before general ones.
- Use Tags and Descriptions: Add meaningful tags and descriptions to rules. This helps with rule management and understanding their purpose.
3. Application-Based Policies
- Leverage App-ID: Palo Alto Firewalls excel at application identification (App-ID). Create policies based on applications rather than just ports and protocols.
- Application Whitelisting: Allow only necessary applications. Block everything else by default.
4. User-Based Policies
- User-ID Integration: Integrate Palo Alto Firewalls with User-ID sources (e.g., Active Directory). Create policies based on user identities.
- Role-Based Access Control: Assign roles to users and enforce policies accordingly.
5. Logging and Monitoring
- Enable Logging: Log traffic for analysis and troubleshooting. Configure log forwarding to a central system.
- Monitor Threats: Set up alerts for suspicious activity. Regularly review logs for anomalies.
6. Security Profiles
- Antivirus and Anti-Spyware Profiles: Enable these profiles to scan traffic for known threats.
- URL Filtering Profiles: Block malicious or inappropriate websites.
7. Regular Audits
- Configuration Audits: Periodically review firewall configurations. Ensure compliance with security standards.
- Rule Cleanup: Remove unused or redundant rules. Simplify your rulebase.
Threat Intelligence Integration
Palo Alto Firewalls stand as stalwarts in the realm of network security, shielding organizations from an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. These robust guardians combine cutting-edge technology with a user-centric approach, making them indispensable for safeguarding digital assets. In this article, we delve into the world of Palo Alto Firewalls, with a particular focus on vulnerabilities and mitigation strategies.
Why Palo Alto Firewalls Matter
- Advanced Threat Prevention: Palo Alto Firewalls go beyond traditional packet filtering. They employ a multi-layered approach, including signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, and machine learning. This arsenal allows them to thwart known and unknown threats, from malware to zero-day exploits.
- Application Visibility and Control: Palo Alto Firewalls provide granular visibility into network traffic. Administrators can identify applications, users, and content flowing through the firewall. This visibility enables precise policy enforcement and prevents unauthorized application usage.
- User-Based Policies: Unlike legacy firewalls that rely solely on IP addresses, Palo Alto Firewalls allow policies based on user identities. This user-centric approach ensures that security rules adapt to individual behavior, enhancing overall protection.
- Integration with Threat Intelligence: Palo Alto Firewalls thrive on real-time threat intelligence. They can seamlessly integrate with threat feeds, providing updates on emerging vulnerabilities. Proactive defense becomes possible by staying ahead of the threat curve.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Palo Alto Firewalls include WAF features. They protect web applications from common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and remote file inclusion.
Vulnerabilities and Palo Alto Firewalls
While Palo Alto Firewalls are robust, no system is entirely immune to vulnerabilities. Regular security assessments, patch management, and adherence to best practices are essential to minimize risks. In subsequent sections, we’ll explore common vulnerabilities, security patch management, and configuration best practices specific to Palo Alto Firewalls.
Logging and Monitoring
Palo Alto Firewalls are the vigilant sentinels of network security, standing guard against cyber threats. But how do they maintain their watchful eye? The answer lies in robust logging and monitoring practices.
The Importance of Logging
- Visibility: Logging captures a detailed record of network traffic, user activity, and security events. It’s like having a security camera for your digital fortress.
- Forensics and Investigations: When an incident occurs, logs provide crucial evidence. They help trace the steps of an attacker, identify vulnerabilities, and assess the impact.
- Compliance and Audits: Many regulations require organizations to maintain logs. Palo Alto Firewalls ensure compliance by logging relevant events.
What to Log
- Traffic Logs: Record details of allowed and denied traffic. Who accessed what, when, and from where?
- Threat Logs: Capture information about detected threats—malware, phishing attempts, and more.
- System Logs: Monitor firewall health, configuration changes, and administrative actions.
Monitoring Strategies
- Real-Time Alerts: Set up alerts for critical events. Receive notifications when something requires immediate attention.
- Log Forwarding: Send logs to a central system (SIEM) for aggregation and analysis. Centralized logging simplifies monitoring.
- Regular Review: Regularly review logs. Look for anomalies, patterns, and signs of compromise.
Web Application Firewall (WAF) Features
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is like a vigilant bouncer at the entrance of your web applications. Its job? To keep out the troublemakers—malicious actors, hackers, and sneaky vulnerabilities. Let’s dive into the key features of a WAF, with a focus on how Palo Alto Firewalls excel in this domain.
1. Application Layer Protection
- Granular Control: WAFs operate at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model. They understand the nuances of HTTP/HTTPS traffic, allowing precise rule enforcement.
- Signature-Based Detection: WAFs recognize known attack patterns (SQL injection, cross-site scripting, etc.) and block them. Palo Alto Firewalls use App-ID to identify applications, making their protection more targeted.
2. Positive and Negative Security Models
- Positive Security Model: Specify what’s allowed. Whitelist legitimate requests. Palo Alto WAFs excel here—they understand your app’s normal behavior and allow only that.
- Negative Security Model: Specify what’s blocked. Blacklist malicious patterns. Palo Alto WAFs combine both models for comprehensive coverage.
3. Custom Rules and Policies
- Tailored Rules: Create custom rules based on your application’s unique requirements. Palo Alto WAFs allow fine-tuning to match your app’s behavior.
- URL Rewriting: Modify URLs to prevent attacks. Palo Alto WAFs can transform incoming requests to safer formats.
4. Bot Protection
- Bot Mitigation: Identify and block malicious bots. Whether it’s scraping, brute force attacks, or automated vulnerability scanning, Palo Alto WAFs keep them at bay.
- Rate Limiting: Control the rate at which requests come in. Prevents abuse and ensures fair resource allocation.
5. Logging and Reporting
- Detailed Logs: Palo Alto WAFs log all events—allowed, blocked, and flagged. These logs are gold for incident response and forensics.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Keep an eye on traffic trends, anomalies, and potential threats. Palo Alto WAFs provide real-time insights.
6. Integration with Threat Intelligence
- Threat Feeds: Palo Alto WAFs can integrate with threat intelligence feeds. Stay updated on emerging threats and adjust your rules accordingly.
Palo Alto PA-400 Series
The PA-400 Series is designed for small organizations or branch offices. Here are some highlights:
- Variety of Models: The series includes several models, such as the PA-410, PA-415, PA-415-5G, PA-440, PA-445, PA-450, PA-455, and PA-460.
- TPM Module: Each firewall in this series comes with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) for secure key storage and enhanced security.
- Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP): Simplify deployment with ZTP, allowing automatic configuration when the firewall is first connected to the network.
- Compact Form Factor: These firewalls are space-efficient, making them ideal for smaller environments.
Palo Alto PA-800 Series
The PA-800 Series strikes a balance between performance and affordability. Key features include:
- Midrange Performance: These firewalls offer solid performance for midsize organizations or distributed sites.
- Multiple Models: The series includes models like the PA-820, PA-850, and PA-820-5G.
- Hardware Encryption Acceleration: Ensures efficient handling of encrypted traffic.
- Flexible Deployment Options: Whether it’s a branch office or a regional hub, the PA-800 Series adapts.
Palo Alto PA-5200 Series
For larger enterprises with demanding security needs, the PA-5200 Series delivers:
- High Performance: These firewalls pack serious horsepower, suitable for data centers and large networks.
- Variety of Models: Choose from models like the PA-5220, PA-5250, and PA-5260.
- Advanced Threat Prevention: Robust security features, including App-ID, User-ID, and WildFire.
- Scalability: The PA-5200 Series grows with your organization’s requirements.
Case Studies: Real-World Vulnerability Examples
Let’s delve into real-world vulnerability examples related to Palo Alto Firewalls. These cases highlight the importance of robust security practices and the impact of vulnerabilities.
1. CVE-2020-2021: PAN-OS Authentication Bypass
- Vulnerability: An authentication bypass vulnerability affected Palo Alto Firewalls running PAN-OS versions prior to 9.1.0.
- Impact: Attackers could bypass authentication and gain unauthorized access to the firewall’s management interface.
- Mitigation: Palo Alto Networks promptly released a security patch. Organizations needed to update their firewalls to the patched version to mitigate the risk.
2. Misconfigured Security Policies
- Scenario: A large enterprise deployed Palo Alto Firewalls across multiple locations. However, misconfigured security policies allowed excessive traffic between zones.
- Impact: Attackers exploited this misconfiguration to move laterally within the network, compromising critical servers.
- Lesson: Regularly review and audit security policies. Ensure they align with the organization’s security requirements.
3. Unpatched Firmware Vulnerabilities
- Case: A financial institution neglected firmware updates for their Palo Alto Firewalls.
- Impact: Attackers exploited known vulnerabilities, leading to unauthorized access and data exfiltration.
- Best Practice: Regularly update firmware to address security issues and enhance resilience.
4. Insufficient Logging and Monitoring
- Incident: A company suffered a data breach, but their Palo Alto Firewall logs were inadequate.
- Impact: The lack of detailed logs hindered incident response and forensic analysis.
- Recommendation: Enable comprehensive logging and real-time monitoring. Logs are invaluable during security incidents.
5. Zero-Day Exploits
- Scenario: A nation-state actor discovered a zero-day vulnerability in Palo Alto Firewalls.
- Impact: They exploited it to gain access to sensitive government networks.
- Preparedness: Organizations must have incident response plans in place to handle zero-day threats swiftly.
In conclusion, Palo Alto Firewalls serve as formidable guardians in the battle against cyber threats. Their advanced threat prevention, user-centric policies, and integration with threat intelligence make them indispensable for securing networks. However, vulnerabilities remain a constant challenge. Regular patch management, proper configuration, and robust logging are essential to maintain their effectiveness. As you navigate the digital landscape, remember that a well-protected network begins with informed choices and proactive security practices. Stay vigilant, stay secure




Pingback: Securing the Future: A Deep Dive into Palo Alto Networks and FortiGate - EstoreAB
Pingback: The Rise of Zero-Trust Architecture in Cloud Environments - EstoreAB
Pingback: Navigating the Currents of Network Traffic with F5 Expertise - EstoreAB