Google Cloud vs. AWS: Navigating the Cloud Giants
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, two titans stand tall: Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS). These behemoths power applications, store data, and fuel innovation across the globe. But which cloud platform suits your needs? In this comprehensive comparison between Google Cloud vs. AWS, we’ll dissect their offerings, pricing models, developer tools, and real-world success stories. Buckle up as we embark on a cloud odyssey!
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the ever-expanding digital landscape, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer. Organizations worldwide rely on cloud services to power their applications, store data, and scale their operations. Two major players dominate this arena: Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS). Let’s dive into the world of cloud giants and explore the nuances that set them apart.
Why Cloud Matters
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s understand why cloud computing matters. Imagine having access to virtually unlimited computing resources without the hassle of managing physical servers. That’s precisely what cloud services offer. Whether you’re a startup, a multinational corporation, or an individual developer, the cloud provides agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Meet the Contenders
Google Cloud
- Google Cloud, powered by the same infrastructure that runs Google’s search engine and YouTube, boasts a robust ecosystem. It offers a wide array of services, including virtual machines, databases, machine learning, and more.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- AWS, pioneered by Amazon, is the undisputed leader in cloud services. With a vast global network of data centers, AWS provides an extensive suite of tools for developers, enterprises, and startups.
Where to Add Images
Consider adding images at the following points:
- Data Centers: Visualize the sprawling data centers that power these cloud services.
- Service Icons: Display icons representing various services (compute, storage, databases) offered by Google Cloud and AWS.
- Comparison Charts: Create side-by-side charts highlighting key differences.
- Use Cases: Illustrate real-world scenarios where organizations benefit from these platforms.
Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, especially when demystifying complex concepts. Let your readers visualize the cloud infrastructure as they embark on this comparison journey
Pricing and Cost Structure
When it comes to choosing between Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS), understanding their pricing models is crucial. Let’s break down the cost structures and explore where each platform shines.
AWS vs. Google Cloud: An Overview
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- Market Share: AWS holds over 30% of the cloud market, making it a dominant force.
- Global Presence: With 24 regions and 77 availability zones, AWS offers unparalleled global coverage.
- Services: AWS provides an extensive range of services, including storage, computing, and networking.
Google Cloud
- Emerging Challenger: Google Cloud, born in 2011, leverages Google’s infrastructure.
- Market Growth: While rapidly growing, it still trails behind AWS in overall market presence.
- Services: Google Cloud’s suite of services competes with AWS, often perceived as more competitively priced.
Comprehensive Service Offerings
Both platforms excel in providing a wide array of services. Here’s a glimpse:
- Compute Services:
- AWS: Features Amazon EC2, AWS Lambda, and Elastic Beanstalk.
- Google Cloud: Offers Google Compute Engine, Google App Engine, and Google Kubernetes Engine.
- Database and Storage Solutions:
- Both platforms offer robust options, but AWS generally provides a more diverse range.
Delving into Pricing Models
When comparing AWS vs. Google Cloud, their pricing strategies play a pivotal role. Here’s what you need to know:
- AWS Pricing:
- Diverse Models: AWS offers various pricing models, including pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and custom pricing.
- Economical Choice: For long-term commitments and larger-scale operations, AWS often emerges as the more economical choice.
- Google Cloud Pricing:
- Competitive Approach: Google Cloud’s pricing is often perceived as competitive.
- Flexibility: It provides flexibility, but understanding nuances is essential for cost-effectiveness.
Where to Add Images
- Comparison Charts: Visualize pricing differences between specific services.
- Pricing Tiers: Illustrate pay-as-you-go vs. reserved instances.
- Use Cases: Show cost implications for different scenarios (e.g., startups vs. enterprises).
Compute Services
When comparing Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS), their compute services play a pivotal role in shaping your cloud infrastructure. Let’s explore the key features of each platform and where you might want to consider adding images for clarity.
Google Cloud Compute Services
1. Google Compute Engine (GCE)
- Virtual Machines: GCE provides scalable virtual machines (VMs) that allow you to run applications and workloads.
- Custom Machine Types: Create VMs with custom CPU and memory configurations.
- Preemptible VMs: Cost-effective short-lived instances for batch processing and data analysis.
2. Google App Engine (GAE)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): GAE lets you build and deploy applications without managing infrastructure.
- Automatic Scaling: Scales based on traffic and demand.
- Supports Multiple Languages: Python, Java, Go, and more.
3. Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- Managed Kubernetes: Simplifies container orchestration.
- Auto Scaling and Load Balancing: Efficiently manage containerized applications.
- Integration with Other Google Services: Seamless integration with BigQuery, Pub/Sub, and more.
AWS Compute Services
1. Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
- Widely Used: EC2 is an industry benchmark for VMs.
- Instance Types: Choose from various instance types (e.g., compute-optimized, memory-optimized).
- Spot Instances: Bid-based pricing for cost savings.
2. AWS Lambda
- Serverless Computing: Execute code in response to events without provisioning servers.
- Event-Driven: Ideal for event-driven workloads (e.g., real-time data processing).
- Granular Billing: Pay only for the compute time used.
3. AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- PaaS for Web Applications: Simplifies deployment and management.
- Multiple Languages Supported: Java, .NET, Python, etc.
- Auto Scaling and Load Balancing: Handles traffic spikes seamlessly.
Where to Add Images
- Architecture Diagrams: Visualize how VMs, containers, and serverless functions interact.
- Comparison Tables: Show a side-by-side comparison of features (e.g., GCE vs. EC2).
- Screenshots: Illustrate the user interfaces for creating instances or deploying applications.
Storage and Databases
When comparing Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS), understanding their storage and database offerings is crucial. Let’s explore the key features of each platform and identify where visual aids can enhance comprehension.
Google Cloud Storage and Databases
1. Google Cloud Storage
- Object Storage: Google Cloud Storage provides scalable, durable, and highly available object storage. It’s ideal for storing unstructured data like images, videos, and backups.
- Multi-Regional Buckets: Distribute data across multiple regions for redundancy and low-latency access.
- Integration with BigQuery: Seamlessly move data between storage and analytics using BigQuery.
2. Google Cloud SQL
- Managed Relational Databases: Google Cloud SQL offers fully managed MySQL and PostgreSQL databases.
- Automated Backups and Patch Management: Focus on your application while Google handles maintenance tasks.
- High Availability: Replication and failover options ensure reliability.
3. Google Cloud Firestore
- NoSQL Document Database: Firestore is a serverless, schema-less database for web and mobile apps.
- Real-time Data Sync: Supports real-time synchronization across devices.
- Scalability: Automatically scales to handle varying workloads.
AWS Storage and Databases
1. Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service)
- Object Storage: S3 is a widely used object storage service.
- Bucket-based Architecture: Create buckets to organize and manage data.
- Data Lifecycle Policies: Set rules for data retention and deletion.
2. Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
- Managed Relational Databases: RDS supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and more.
- Automated Backups and Scaling: Easily scale your database as needed.
- Multi-AZ Deployment: High availability with automatic failover.
3. Amazon DynamoDB
- NoSQL Key-Value Database: DynamoDB is fully managed and highly available.
- Scalability: Scales horizontally to handle massive workloads.
- Pay-Per-Usage Pricing: Pay only for what you consume.
Where to Add Images
- Architecture Diagrams: Visualize how data flows between storage buckets, databases, and applications.
- Comparison Tables: Show a side-by-side comparison of features (e.g., Google Cloud Storage vs. Amazon S3).
- Screenshots: Illustrate the user interfaces for creating databases or managing storage.
Networking and Content Delivery
In the realm of cloud computing, networking and content delivery play a crucial role in ensuring seamless connectivity and optimal performance. Let’s explore how Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS) handle these critical aspects, and I’ll highlight where visual aids can enhance understanding.
Google Cloud Networking and Content Delivery
1. Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- Isolated Networks: VPCs allow you to create isolated networks within Google Cloud.
- Custom IP Ranges: Define your own IP address ranges for better control.
- Subnetting: Divide your VPC into subnets for efficient resource management.
2. Google Cloud Load Balancing
- Global Load Balancing: Distributes traffic across multiple regions for high availability.
- HTTP(S), TCP, and UDP Load Balancers: Choose the right type based on your application needs.
- Content Delivery: Google Cloud CDN integrates seamlessly with load balancers for faster content delivery.
AWS Networking and Content Delivery
1. Amazon VPC
- Isolated Networks: VPCs provide isolated network environments within AWS.
- Subnet Configuration: Define public and private subnets for secure communication.
- Network ACLs and Security Groups: Control inbound and outbound traffic.
2. AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
- Classic Load Balancer: Distributes traffic across EC2 instances.
- Application Load Balancer (ALB): Works at the application layer (HTTP/HTTPS).
- Network Load Balancer (NLB): Operates at the transport layer (TCP/UDP).
Where to Add Images
- Network Topology Diagrams: Visualize VPCs, subnets, and load balancers.
- Load Balancer Architecture: Show how traffic flows through load balancers.
- Content Delivery Flow: Illustrate how CDN caches and delivers content globally.
Security and Compliance
When evaluating Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS), security becomes paramount. Both cloud providers prioritize data protection and compliance. Let’s delve into their security features and where visual aids can enhance understanding.
Shared Responsibility Model
Before we dive into specifics, let’s understand the shared responsibility model. In cloud computing, security is a joint effort between the provider (Google Cloud or AWS) and the customer (you). Here’s how it breaks down:
- Customer Responsibility:
- Protecting your data, user accounts, and applications.
- Configuring security settings within your cloud resources.
- Compliance with industry standards.
- Cloud Provider Responsibility:
- Securing the underlying infrastructure (physical hosts, storage, networking).
- Ensuring data center security.
Google Cloud Security
1. Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Granular Access Control: IAM allows fine-grained permissions management.
- Service Accounts: Create service accounts for applications and services.
- Security Best Practices: Google follows industry standards and provides guidelines.
2. Encryption at Rest and in Transit
- Data Encryption: Google encrypts data both at rest (in storage) and in transit (over networks).
- Key Management: Google Cloud Key Management Service (KMS) for managing encryption keys.
AWS Security
1. AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Access Policies: IAM enables you to control access to AWS resources.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhance security for user accounts.
- Resource-Level Permissions: Fine-tune access permissions.
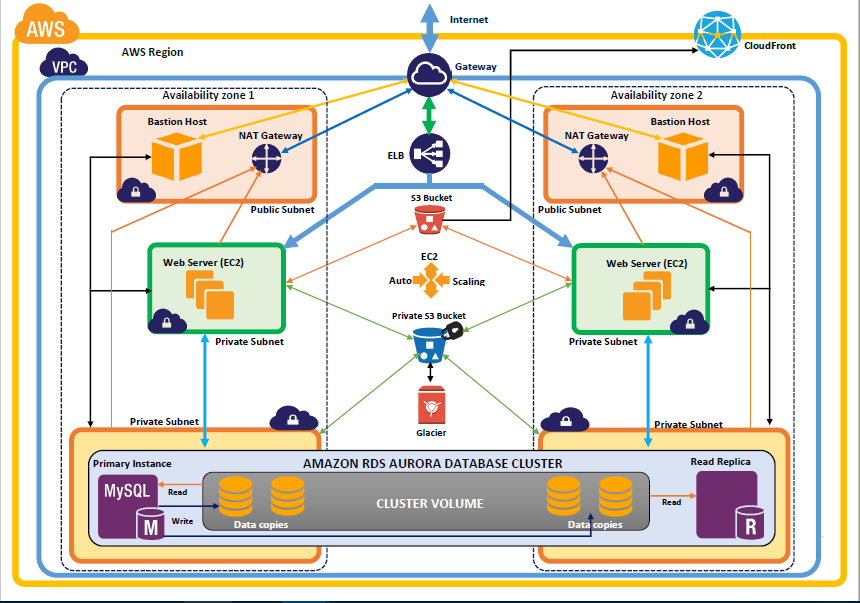
2. Encryption Services
- Amazon S3 Encryption: Encrypt data stored in Amazon S3 buckets.
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS): Manage encryption keys.
- SSL/TLS for Network Traffic: Secure data in transit.
Compliance Considerations
Both platforms comply with various standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001). Consider adding images at these points:
- Shared Responsibility Model: Visualize the division of responsibilities.
- Encryption Flow: Show how data is encrypted at rest and during transmission.
- Compliance Badges: Display certifications (GDPR, SOC 2, etc.).
Machine Learning and AI Services
In the dynamic landscape of cloud computing, machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) have emerged as powerful tools. Both Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS) offer robust services in this domain. Let’s explore their offerings and identify where visual aids can enhance comprehension.
Understanding AI and ML
- AI vs. ML:
- AI aims to simulate human thought and decision-making.
- ML is a subset of AI that enables computers to learn from data without explicit programming.
- Essential Ingredients for ML:
- Data: Massive amounts of data are crucial.
- Computation/Algorithms: Apply algorithms to the data.
- Knowledge: Understand ML concepts.
Machine Learning Building Blocks
- Speech to Text and Text to Speech:
- Convert spoken language to text and vice versa.
- Use cases: Voice assistants, transcription services.
- Visual Aid: Flowchart showing the process.
- Chatbots:
- Create conversational interfaces.
- Use cases: Customer support, virtual assistants.
- Visual Aid: Chatbot interaction diagram.
- Translation:
- Translate text between languages.
- Use cases: Multilingual applications.
- Visual Aid: Language flags representing translation.
- Text Analytics:
- Extract insights from text data.
- Use cases: Sentiment analysis, topic modeling.
- Visual Aid: Word cloud showing key terms.
- Document Analysis:
- Extract information from documents.
- Use cases: OCR, form extraction.
- Visual Aid: Sample document with highlighted fields.
- Image and Video Analysis:
- Analyze visual content.
- Use cases: Object detection, facial recognition.
- Visual Aid: Image with bounding boxes.
- Anomaly Detection:
- Identify unusual patterns.
- Use cases: Fraud detection, network security.
- Visual Aid: Line chart with anomalies marked.
- Personalization:
- Customize user experiences.
- Use cases: Recommendations, targeted ads.
- Visual Aid: User profile with personalized content.
Machine Learning Platforms
- Guided Model Development:
- Step-by-step model creation.
- Use cases: Predictive analytics, recommendation engines.
- Visual Aid: Workflow diagram.
- Full ML Workbench:
- End-to-end ML pipelines.
- Use cases: Data preprocessing, model training, deployment.
- Visual Aid: Pipeline flowchart.
- MLOps:
- DevOps for ML.
- Use cases: Model versioning, monitoring.
- Visual Aid: CI/CD pipeline for ML.
- Augmented AI:
- Human-AI collaboration.
- Use cases: Labeling data, model validation.
- Visual Aid: Human-AI handshake.
Machine Learning Infrastructure
- Hardware:
- GPUs, TPUs for accelerated training.
- Use cases: Deep learning, large-scale models.
- Visual Aid: GPU cluster.
- Explainability and Bias:
- Understand model decisions.
- Use cases: Fairness, interpretability.
- Visual Aid: Model heatmap highlighting bias.
Where to Add Images
- Flowcharts: Visualize ML processes (e.g., speech-to-text).
- Sample Outputs: Show translated text, detected objects.
- Architecture Diagrams: Explain ML platforms and infrastructure.
Developer Tools and Integration
When it comes to building and managing applications in the cloud, developer tools and integration play a crucial role. Let’s explore how Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS) empower developers, and I’ll highlight where visual aids can enhance understanding.
Google Cloud Developer Tools
- Google Cloud SDK (gcloud):
- Command-line interface for managing Google Cloud resources.
- Use cases: Deploying applications, managing VMs, and configuring services.
- Visual Aid: Screenshot of the gcloud command prompt.
- Cloud Shell:
- Browser-based shell environment with pre-installed tools.
- Use cases: Quick access to gcloud, Git, and other utilities.
- Visual Aid: Cloud Shell interface.
- Cloud Build:
- Continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) service.
- Use cases: Automate build, test, and deployment pipelines.
- Visual Aid: Pipeline diagram.
- Cloud Functions:
- Serverless compute platform for event-driven code.
- Use cases: Respond to HTTP requests, process data.
- Visual Aid: Function trigger flowchart.
AWS Developer Tools
- AWS CLI (Command Line Interface):
- Unified tool for managing AWS services.
- Use cases: Scripting, automation, and resource management.
- Visual Aid: Screenshot of AWS CLI commands.
- AWS CodePipeline:
- CI/CD service for building, testing, and deploying code.
- Use cases: End-to-end automation of release pipelines.
- Visual Aid: Pipeline visualization.
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk:
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) for deploying applications.
- Use cases: Simplified app deployment and scaling.
- Visual Aid: Elastic Beanstalk dashboard.
- AWS Lambda:
- Serverless compute service for running code in response to events.
- Use cases: Event-driven microservices, data processing.
- Visual Aid: Lambda function architecture.
Integration Capabilities
- Google Cloud Pub/Sub:
- Messaging service for asynchronous communication.
- Use cases: Decoupling components, event-driven architectures.
- Visual Aid: Pub/Sub topic and subscription.
- AWS Step Functions:
- Coordinate multiple AWS services into serverless workflows.
- Use cases: Orchestration of complex tasks.
- Visual Aid: Step Functions state machine.
Where to Add Images
- Screenshots: Show the actual developer tools interfaces.
- Architecture Diagrams: Explain how services integrate and interact.
- Command Examples: Display code snippets for CLI usage.
Support and Documentation
When navigating the vast cloud ecosystem, support and documentation become your trusted companions. Let’s explore how Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS) assist users, and I’ll highlight where visual aids can enhance understanding.
Google Cloud Support
- Support Plans:
- Basic: Access to documentation, community forums, and billing support.
- Silver, Gold, and Platinum: Gradually increasing levels of technical support.
- Visual Aid: Comparison table showing support features.
- Documentation:
- Cloud Docs: Comprehensive guides, tutorials, and best practices.
- API Reference: Detailed information on services and APIs.
- Visual Aid: Screenshot of a documentation page.
- Community Forums:
- Stack Overflow: Active community for Q&A.
- Google Groups: Discussion forums for specific topics.
- Visual Aid: Stack Overflow logo.
AWS Support
- Support Plans:
- Basic: Access to documentation and community forums.
- Developer, Business, and Enterprise: Increasing levels of support.
- Visual Aid: AWS Support tiers diagram.
- Documentation:
- AWS Documentation: Extensive library covering services, SDKs, and tools.
- Whitepapers: In-depth technical resources.
- Visual Aid: AWS documentation landing page.
- Community Forums:
- AWS Developer Forums: Engage with other developers.
- Reddit (r/aws): Active community discussions.
- Visual Aid: Reddit logo.
Where to Add Images
- Support Plans Comparison: Visualize the differences between support tiers.
- Documentation Landing Page: Show the wealth of available resources.
- Community Logos: Display logos of relevant forums.
Case Studies and Use Cases
Let’s delve into real-world scenarios where Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS) have made a significant impact. These case studies and use cases demonstrate how organizations leverage these platforms to achieve their goals.
Google Cloud Success Stories
- Snap Inc. (Snapchat):
- Use Case: Scalability and reliability for multimedia messaging.
- Solution: Snap runs on Google Cloud, handling millions of daily active users.
- Visual Aid: Screenshot of Snapchat’s interface.
- Spotify:
- Use Case: Music streaming at scale.
- Solution: Spotify relies on Google Cloud for data storage, analytics, and recommendation algorithms.
- Visual Aid: Spotify logo alongside Google Cloud services.
- Airbnb:
- Use Case: Dynamic pricing and search recommendations.
- Solution: Airbnb uses Google Cloud’s BigQuery for data analysis and machine learning.
- Visual Aid: Airbnb booking flow.
AWS Customer Stories
- Netflix:
- Use Case: Streaming entertainment globally.
- Solution: Netflix’s entire infrastructure runs on AWS, ensuring high availability and scalability.
- Visual Aid: Netflix homepage.
- NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL):
- Use Case: Space exploration and scientific research.
- Solution: JPL uses AWS for data processing, simulations, and Mars rover missions.
- Visual Aid: Mars rover image.
- General Electric (GE):
- Use Case: Industrial IoT and predictive maintenance.
- Solution: GE leverages AWS for analyzing sensor data from turbines and equipment.
- Visual Aid: Industrial machinery with sensors.
Where to Add Images
- Screenshots: Showcase the interfaces of applications like Snapchat and Spotify.
- Logos: Display logos of companies (Netflix, Airbnb, GE) alongside cloud providers.
- Use Case Visuals: Illustrate scenarios (e.g., Mars rover, industrial machinery).
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services (AWS), let’s reflect on the key takeaways. These cloud giants offer unparalleled capabilities, but choosing the right fit depends on your specific needs.
Considerations for Decision-Making
- Workload Type:
- Google Cloud: Ideal for data analytics, machine learning, and app development.
- AWS: Versatile for a wide range of workloads, from startups to enterprises.
- Pricing Strategy:
- Google Cloud: Often competitive, especially for sustained usage.
- AWS: Offers diverse pricing models, including pay-as-you-go and reserved instances.
- Developer Experience:
- Google Cloud: User-friendly interfaces, Cloud Shell, and robust SDKs.
- AWS: Rich ecosystem with extensive documentation and developer tools.
Visualizing the Cloud Journey
- Choose Your Path:
- Whether you’re building the next big app or launching a satellite, both platforms have you covered.
- Visual Aid: Diverging paths representing Google Cloud and AWS.
- Scale New Heights:
- Scalability is key. Both platforms allow you to scale horizontally and vertically.
- Visual Aid: Mountain peaks symbolizing growth.
- Security Umbrella:
- Security is non-negotiable. Both Google Cloud and AWS prioritize data protection.
- Visual Aid: Security shield enveloping cloud services.
Your Cloud Odyssey Awaits
Remember, the cloud journey is an adventure. Explore, experiment, and find your cloud constellation. Whether you choose Google Cloud or AWS, may your deployments be seamless, your APIs responsive, and your infrastructure resilient.
Bon voyage! 🌟🚀




Pingback: Unlocking Success: Essential Tips for Finding Good Software - EstoreAB
Pingback: Palo Alto Firewalls Unleashed: Navigating Vulnerabilities and Resilience - EstoreAB
Pingback: Chronicles of the Cloud: Exploring IT Innovations - EstoreAB